When you start working on web development, you often see http://localhost:3000 on your browser screen. It looks simple, yet it holds powerful meaning. It represents your computer acting like a server. It helps you test websites, web apps, and backend services locally before going live.
Now, let’s explore how http://localhost:3000 works, why developers use it, and how you can fix common issues when it stops responding. This guide gives you deep answers in easy words.
What Is http://localhost:3000
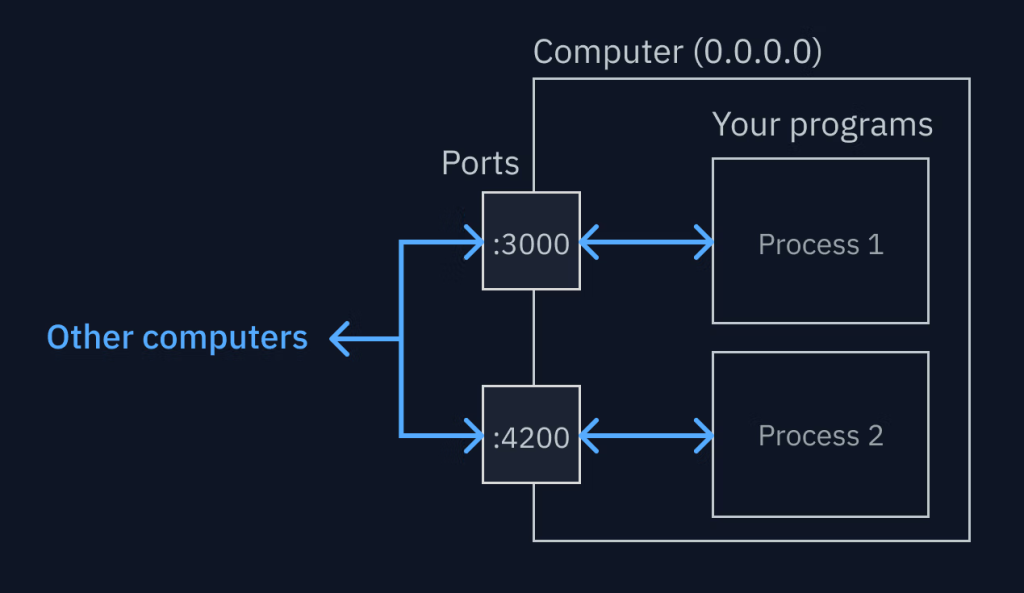
Simply put, http://localhost:3000 is a local address. It lets your browser connect to a web application running on your computer. The term “localhost” refers to your own device. Meanwhile, “3000” is the port number where the server listens for requests.
How http://localhost:3000 Works
First, your development server starts using Node.js, React, Next.js, or another tool. Then, it runs on port 3000. After that, your browser connects to http://localhost:3000 and displays the web app. This process happens only on your computer, meaning no one else can see it unless you allow access.
Why Developers Use Port 3000
Developers choose port 3000 because it’s free, common, and rarely used by other services. Moreover, frameworks like React and Express automatically pick this port. Consequently, beginners and professionals find it easy to remember and use regularly.
Setting Up http://localhost:3000 in React
React makes server setup simple. First, install Node.js. Next, create a React app using the command npx create-react-app my-app. After that, open the project folder and run npm start. Immediately, your browser opens http://localhost:3000, and your app appears.
Using http://localhost:3000 in Next.js
Next.js follows a similar pattern. Start by typing npx create-next-app. Then, run npm run dev. Soon, your development server launches. After that, open your browser and visit http://localhost:3000 to view your site. This method supports server-side rendering, which boosts speed and performance.
Testing APIs on http://localhost:3000
You can test backend APIs using this port. For example, Express.js can create a simple API. Then, the app listens on port 3000. Consequently, developers open http://localhost:3000/api to test responses. Tools like Postman or Thunder Client help send requests and check data easily.
Common Errors on http://localhost:3000
Sometimes, you face problems like:
- The page not loading
- Port already in use
- Server crashing unexpectedly
Usually, another app occupies port 3000. Therefore, you must stop it or change the port. Alternatively, restart your server or clear the cache. Quick actions solve most issues.
Fixing “Port 3000 Already in Use” Error

If the port is busy, change it immediately. You can update your script by adding PORT=4000 npm start. As a result, the server runs on http://localhost:4000. Another way is shutting down the existing process using terminal commands.
Speed Optimization on http://localhost:3000
Speed matters. Therefore, remove heavy files, compress images, and enable hot reloading. Moreover, clean unnecessary console logs. After that, your local server responds faster and feels more powerful during development.
Security Tips for http://localhost:3000
Even though localhost is private, safety still matters. So, avoid exposing your server publicly without proper security. Never store real passwords or sensitive user data in plain code. Instead, use environment variables. This simple step protects your projects.
Can Others Access http://localhost:3000
By default, no one else can view it. However, sharing tools like Ngrok allow secure public access. First, you start your server. Then, run Ngrok. Immediately, it creates a temporary link. Finally, share that link with others for testing or feedback.
Advanced Customization on Port 3000
You can customize your setup easily. For instance:
- Change port number
- Enable HTTPS instead of HTTP
- Edit proxy settings for API calls
These tweaks improve flexibility. After that, your workflow becomes smoother and more secure.
Conclusion
Now you know how http://localhost:3000 works, why it’s important, and how to fix common errors. Start using it confidently in your projects. Test apps, build APIs, and improve performance. Don’t wait. Open your terminal, run your server, and bring your ideas to life.
FAQs
Q1: What does http://localhost:3000 mean?
It means your browser connects to a local server running on your computer at port 3000.
Q2: Why is port 3000 commonly used?
Port 3000 is popular because most development frameworks use it by default and it rarely causes conflicts.
Q3: How do I change port 3000 to another port?
You can set a new port in your environment file or run commands like PORT=4000 npm start.
Q4: Is localhost safe to use?
Yes, it’s safe when used locally. However, avoid exposing it publicly without proper security measures.
Q5: What if http://localhost:3000 doesn’t load?
Check if the server is running, ensure the port isn’t used by another app, and restart your development environment.